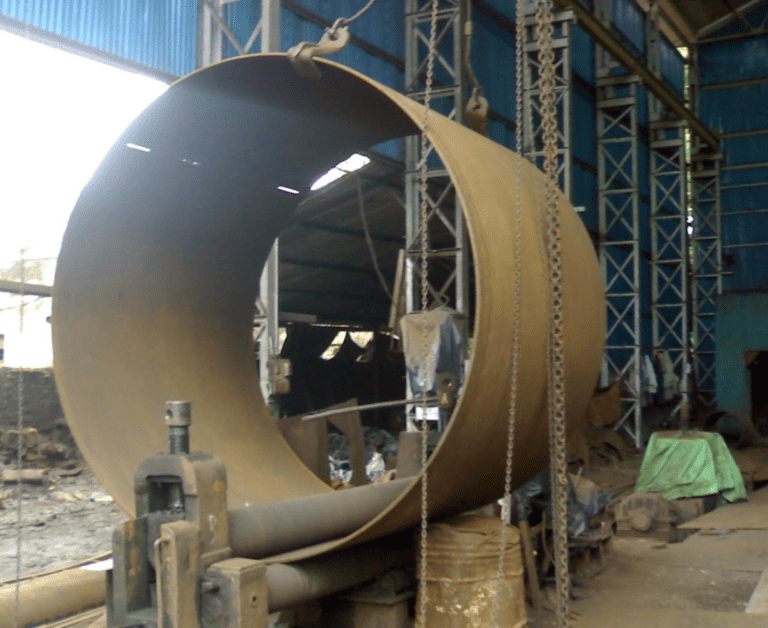
PLATE BLENDING
Rolling is another common method used for plate bending, especially for large-diameter cylinders and curved sections.
The metal plate is passed through a set of rollers that exert pressure on the plate, causing it to gradually bend into the desired shape.
The curvature of the plate is determined by adjusting the distance between the rollers.
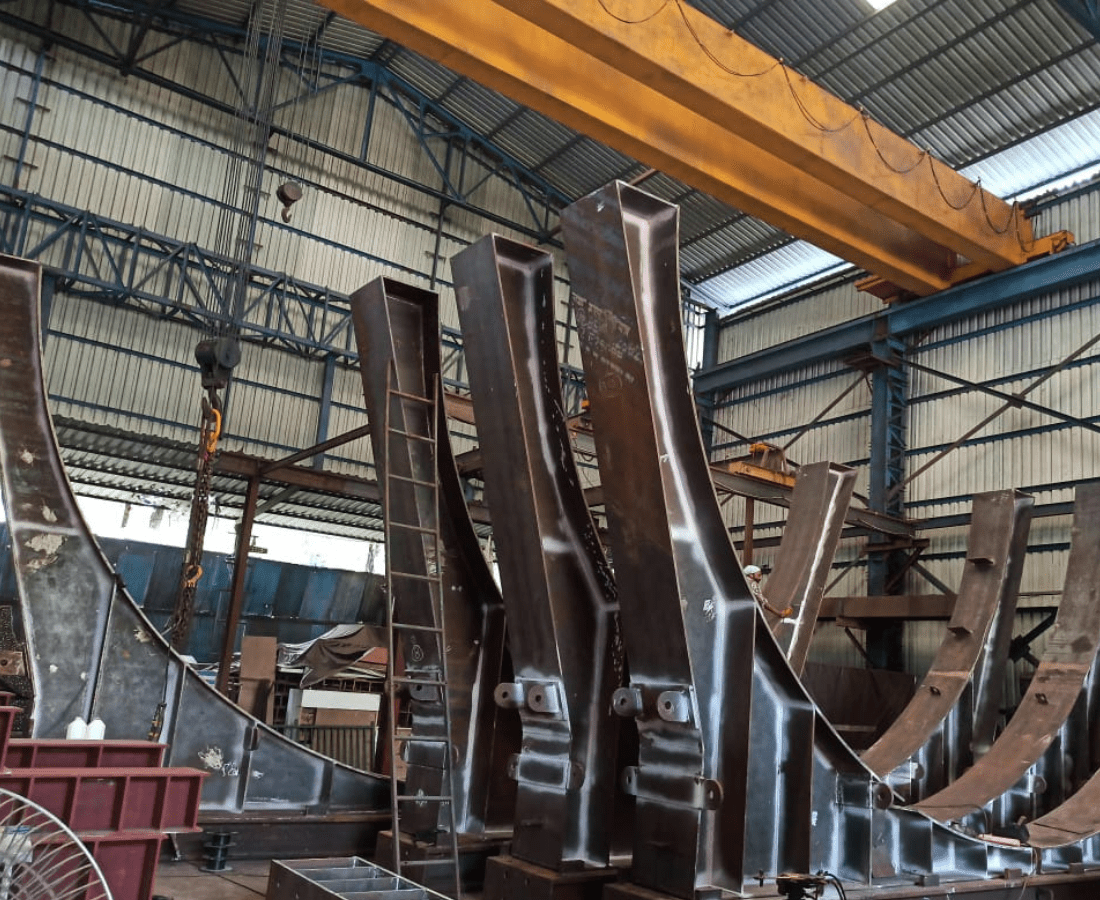


SADDLES
In the fabrication of pressure vessels, a saddle serves as a critical component that provides support and stability to the vessel. The saddle is a structural element designed to cradle the bottom portion of the pressure vessel, distributing its weight and ensuring proper load transfer to the supporting structure. Typically fabricated from materials such as carbon steel or alloys compatible with the vessel’s construction, the saddle plays a crucial role in maintaining the vessel’s integrity under varying operating conditions. Its design must consider factors such as vessel weight, dimensions, and pressure distribution to prevent deformation or damage.
TUNDISH
In metal casting and metallurgy, a “tundish” is a refractory-lined vessel or intermediary container used to control the flow of molten metal. The tundish plays a crucial role in the continuous casting process, where it acts as a buffer between the ladle and the mold. Here are some key points about the tundish in the context of metal fabrication:The tundish is an essential component in continuous casting, a method used to produce metal products with a constant cross-section, such as steel billets, slabs, or blooms. In this process, molten metal is continuously poured from a ladle into the tundish and then directed through a series of molds to solidify into the desired shape.


M S FABRICATION
Mild steel fabrication involves working with mild steel, a type of carbon steel that is often used in various construction and manufacturing applications due to its versatility, strength, and affordability.
Mild steel is available in various forms, including sheets, plates, bars, and tubes. Cut the steel material to the required dimensions using tools such as saws, shears, or CNC plasma cutters.Develop detailed engineering drawings or plans that outline the specifications of the fabricated structure.Shape the mild steel components using bending machines, press brakes, or rollers. This step is crucial for creating angles, curves, or specific profiles within the fabricated structure.
M S STRUCTURE FABRICATION
Structure fabrication is the process of creating metal or steel structures for various applications.. Welding and joining techniques are commonly employed to assemble the structural components, ensuring stability and strength. Quality control measures, such as non-destructive testing, are implemented to guarantee the integrity of the fabricated structure. The final step involves surface treatment, such as painting or galvanizing, to enhance durability and protect against corrosion, ensuring the longevity of the fabricated structure in diverse industries like construction and manufacturing.
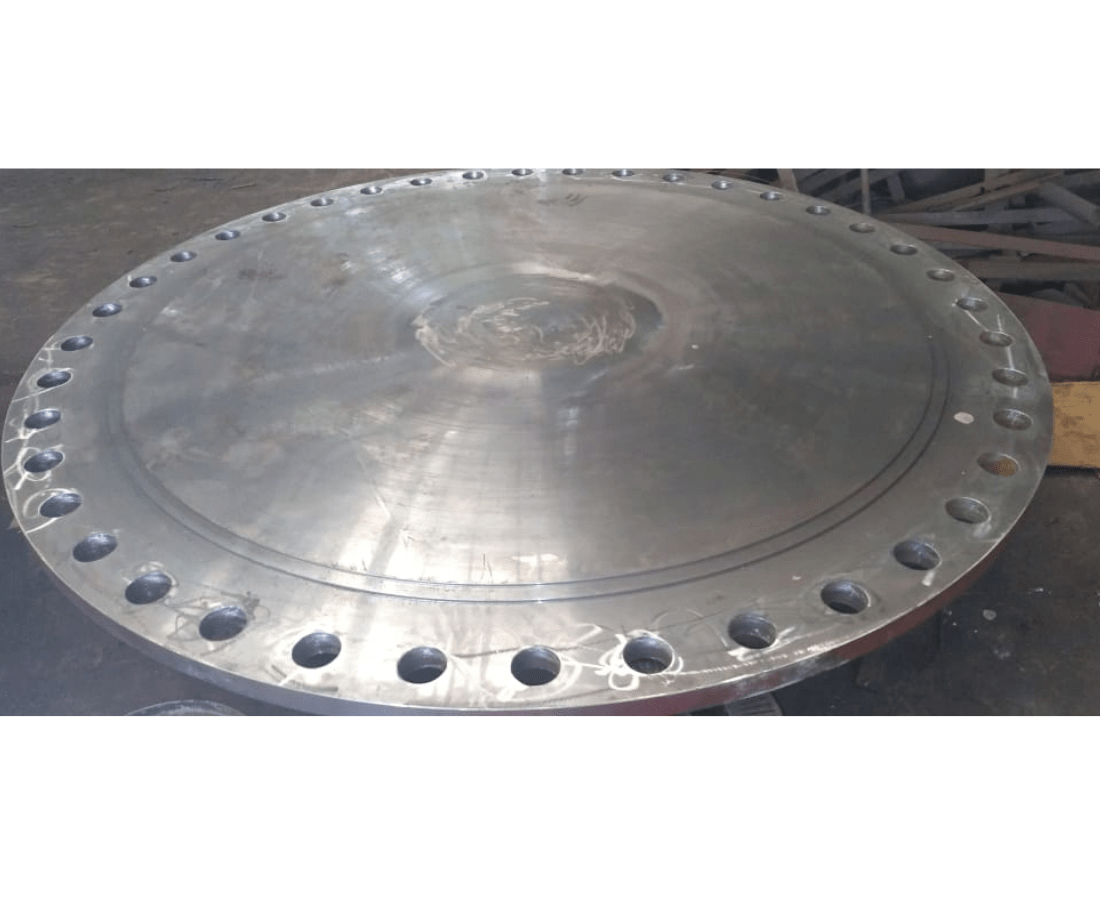


FLANGES
Flanges are essential components in piping systems, serving as connectors for pipes, valves, and other equipment. These flat, circular discs with bolt holes allow for the easy assembly and disassembly of pipes, facilitating maintenance and modifications. Flanges come in various types, such as weld neck, slip-on, and blind flanges, each designed for specific applications. The bolted connection between flanges creates a tight seal, preventing leaks and ensuring the integrity of the pipeline. Flanges are crucial in industries such as oil and gas, chemical, and manufacturing, where they provide a reliable and versatile means of joining piping components in a wide range of configurations.
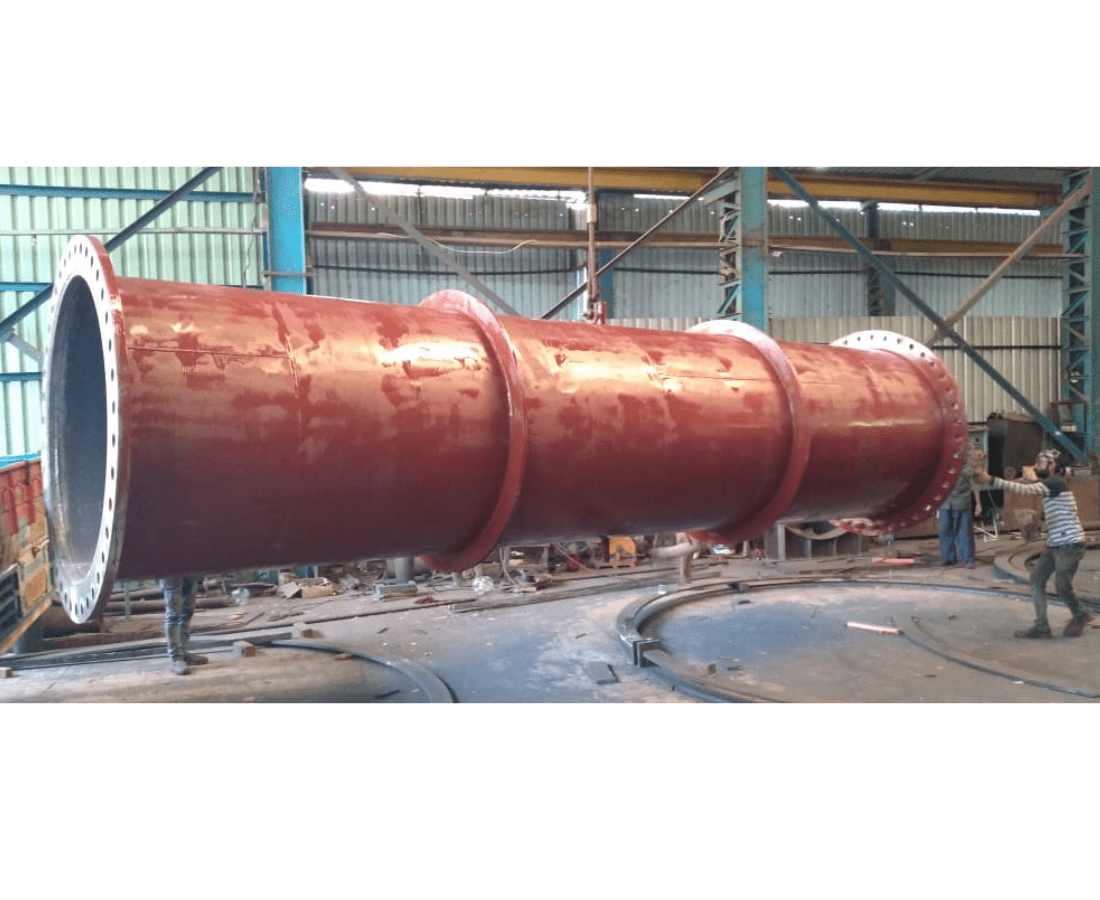
DUMMY SHELL
A cylindrical shell in the context of fabrication typically refers to a component or structure that is shaped like a cylinder. Cylindrical shells are commonly used in various engineering and manufacturing applications due to their strength, stability, and efficiency in handling certain types of loads.
Cylindrical shells are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and aerospace for applications ranging from storage tanks and pressure vessels to structural components. The fabrication process is tailored to the specific requirements of the project and the characteristics of the material being used.

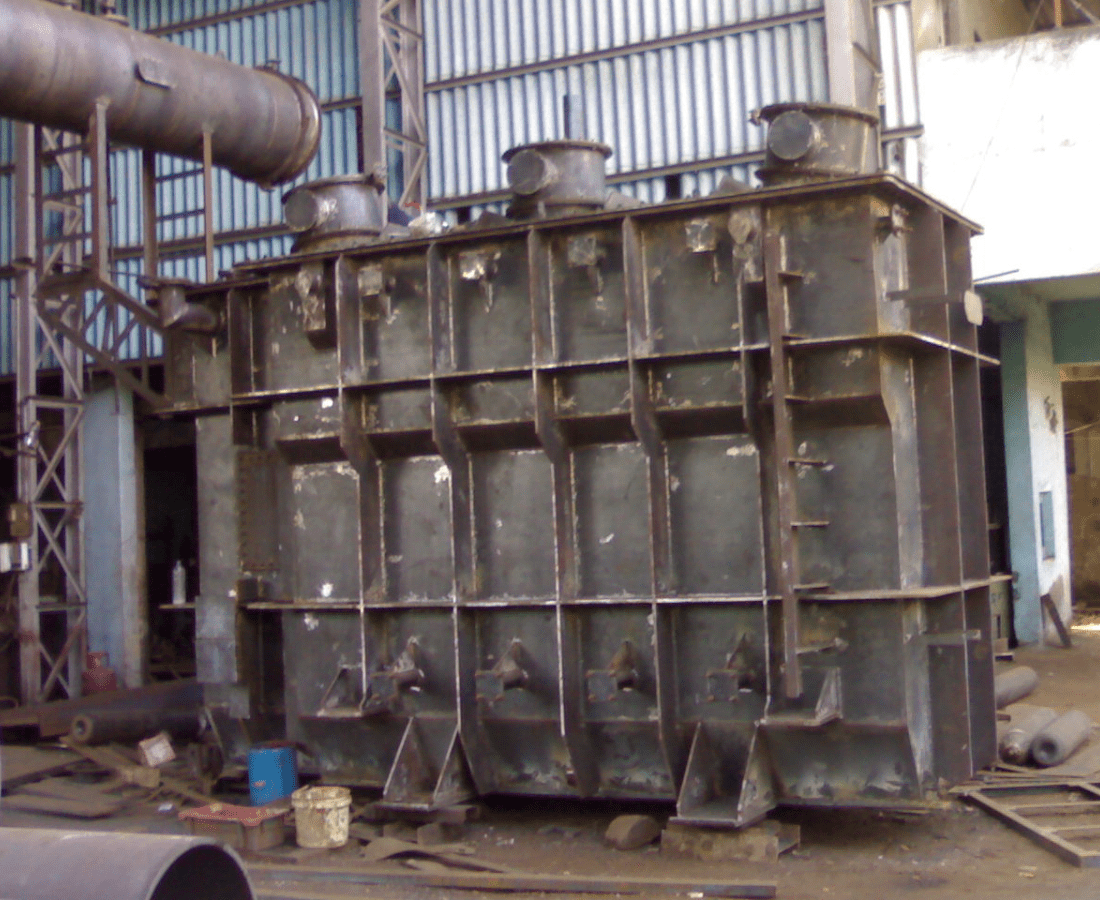
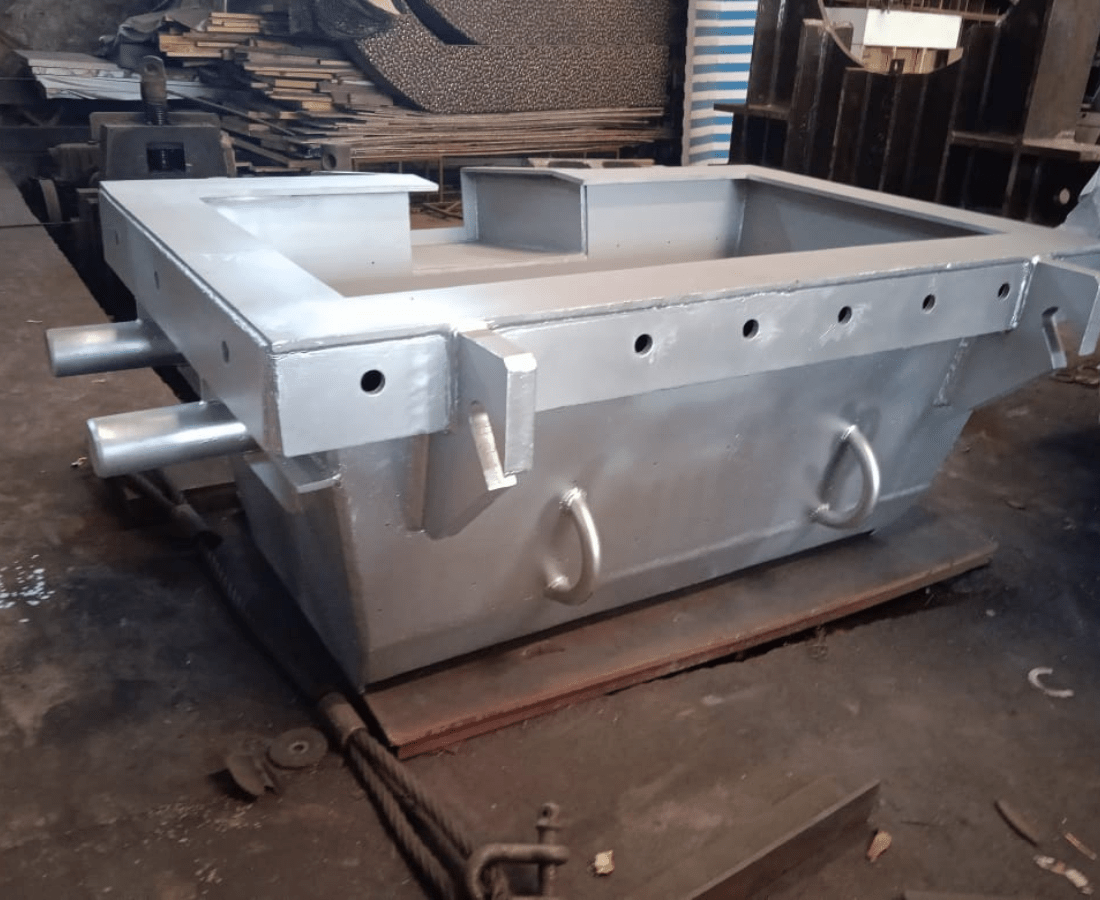
TRANSFORMER TANK
A transformer tank is a crucial component in electrical power systems, designed to house and cool the transformer core and windings. Constructed with durable materials like steel, the tank provides a sealed environment to prevent contamination and oxidation of the transformer oil, ensuring optimal insulation and cooling performance. Additionally, transformer tanks are equipped with accessories such as conservators, breather devices, and oil level indicators to maintain the transformer’s operational efficiency and reliability. Regular maintenance, including oil filtration and tank inspections, is essential to prolong the lifespan of the transformer and ensure its consistent performance in power distribution networks.
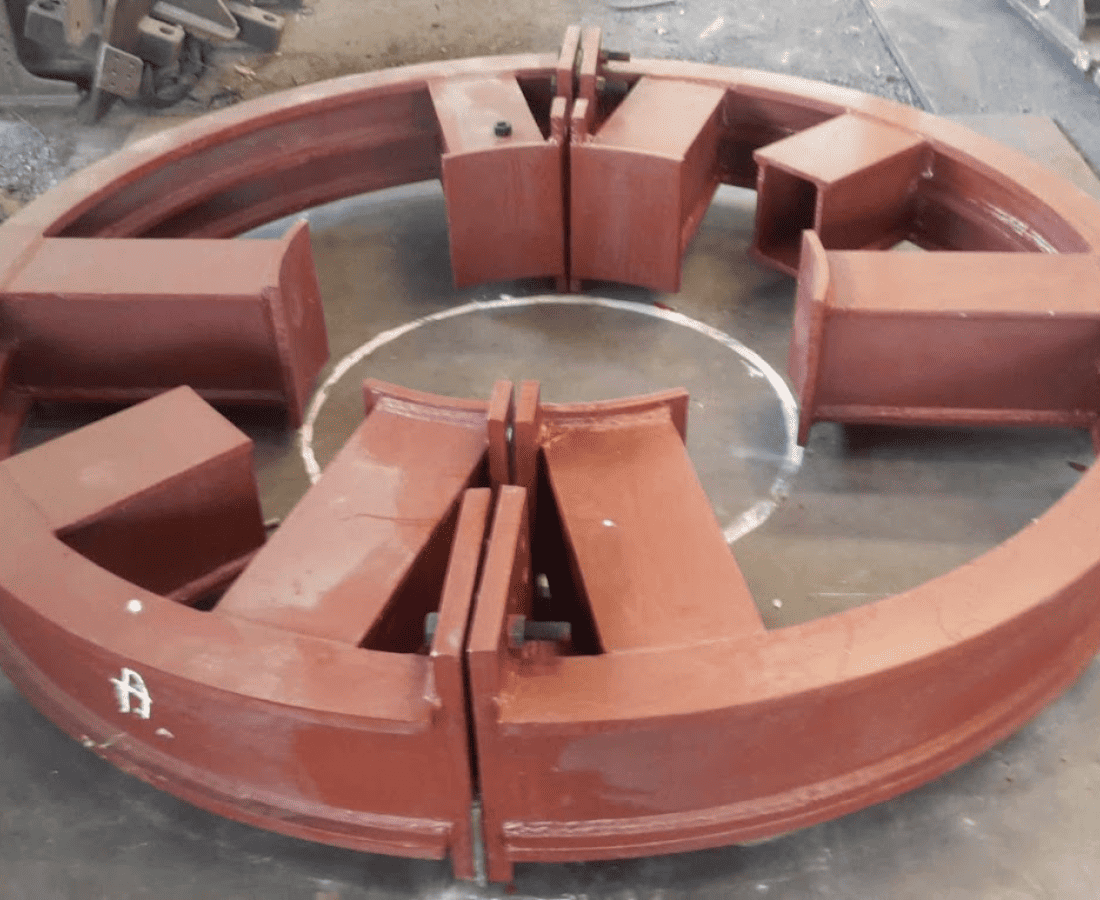
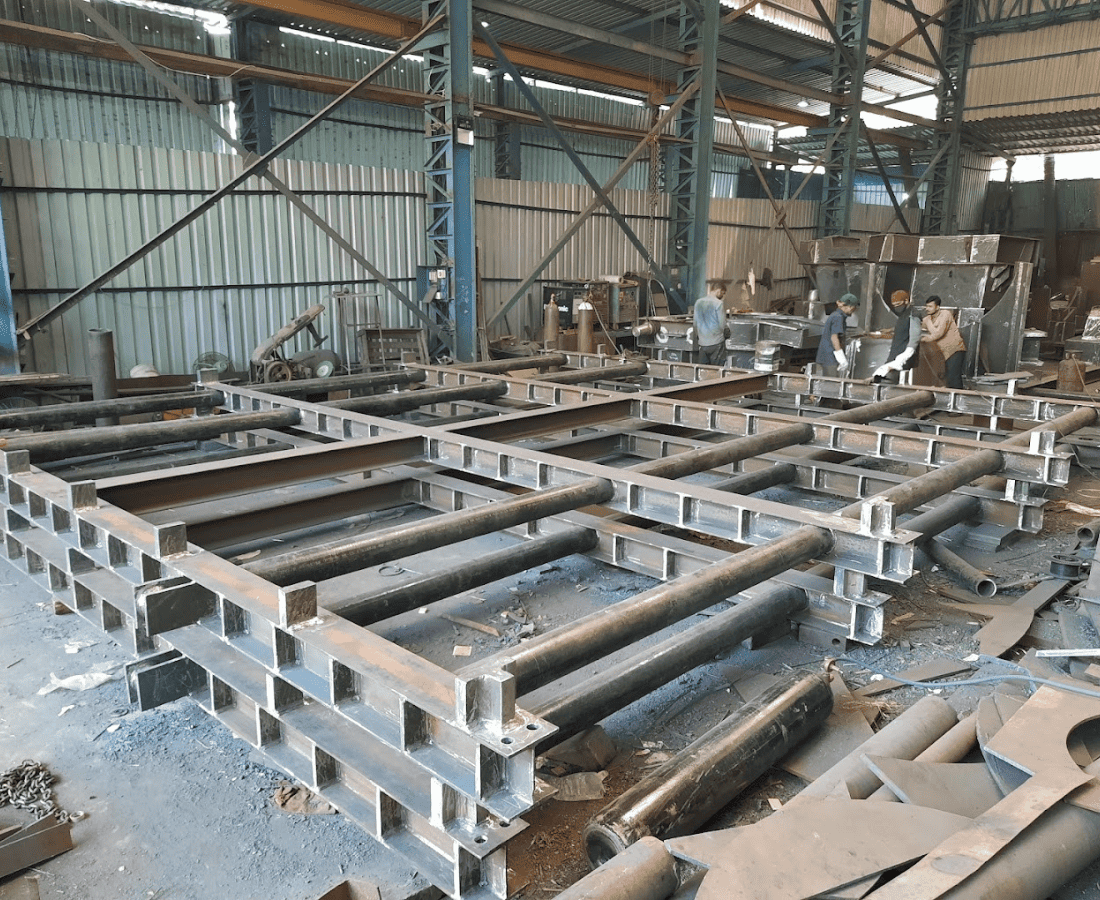
TRANSFORMER FRAME AND FRAME PARTS
The transformer frame serves as the structural support for the core and winding components within an electrical transformer. Typically made of sturdy materials such as steel, the frame provides rigidity and stability to the entire transformer assembly. It also facilitates the proper alignment and positioning of the core and winding structures, crucial for optimal electrical performance. Various frame parts, including yokes, legs, and bracings, are intricately designed to distribute mechanical forces and minimize vibrations during operation. The construction and assembly of these frame elements play a vital role in maintaining the structural integrity and functionality of the transformer.
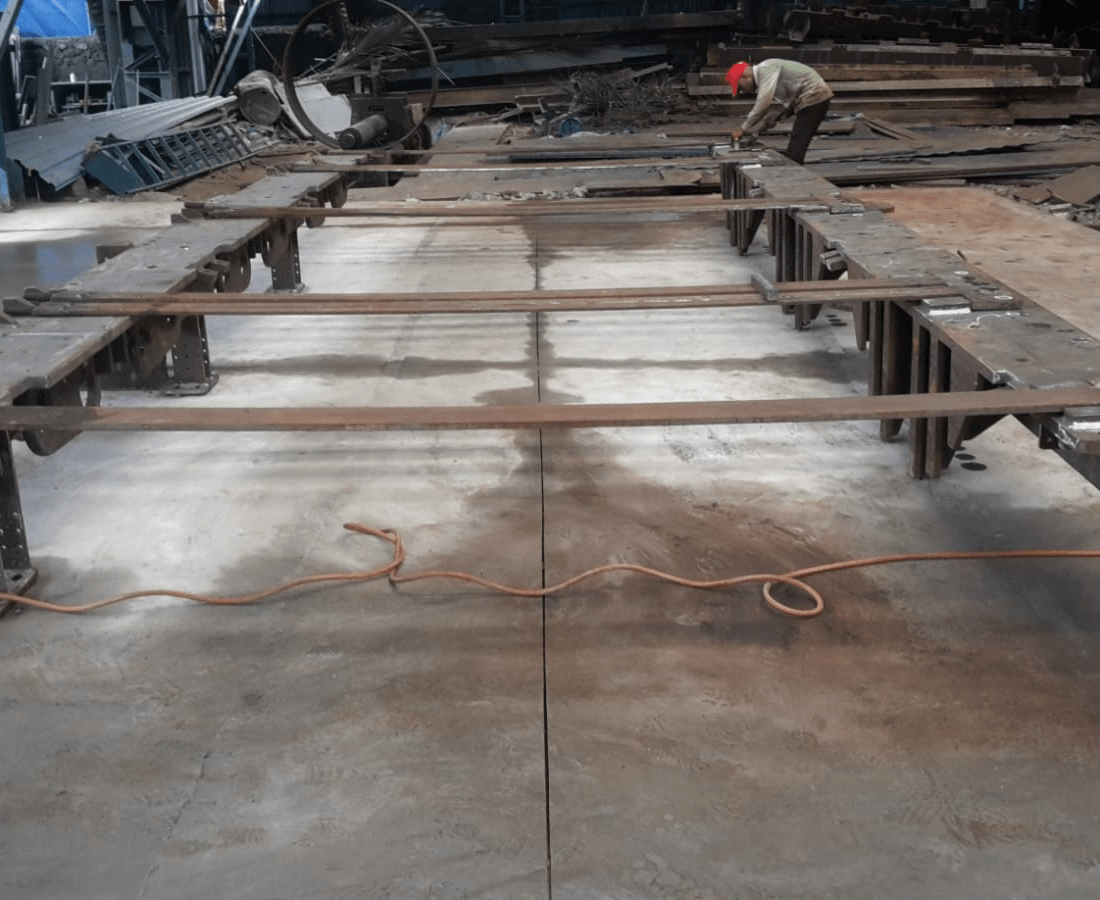
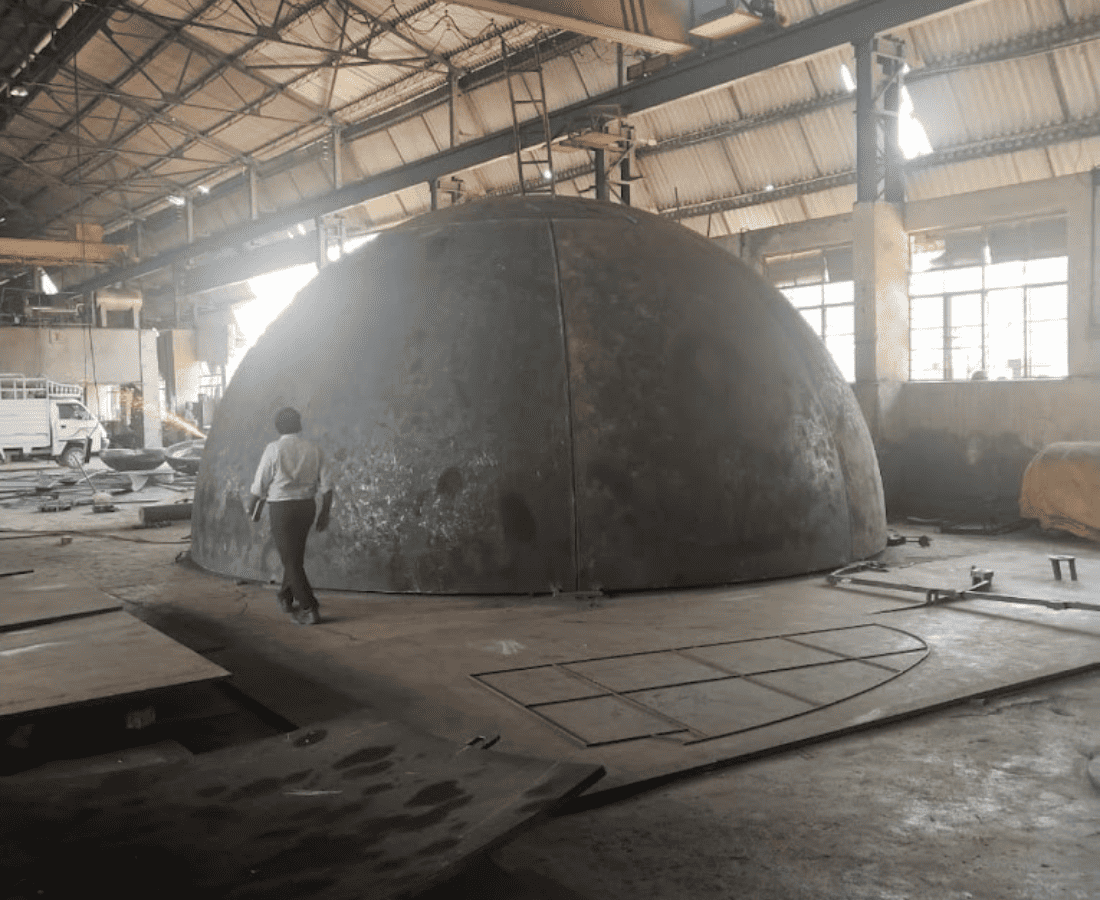


Dish End
A dished end, also known as a dish end or head, is a type of pressure vessel component used in the fabrication of tanks and vessels. It is typically a circular end closure that is welded to the open ends of cylindrical or spherical pressure vessels. Dished ends are designed to accommodate the shape of the vessel and provide structural strength to withstand internal pressure.Dished ends play a critical role in the structural integrity of pressure vessels, and their design and fabrication must comply with relevant engineering codes and standards to ensure the safety of the vessel in service.
